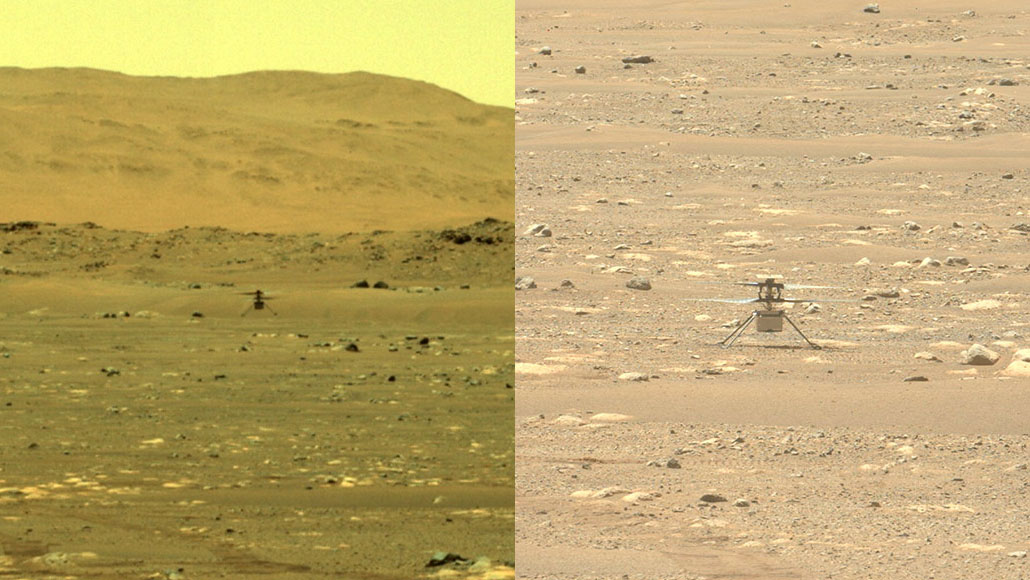

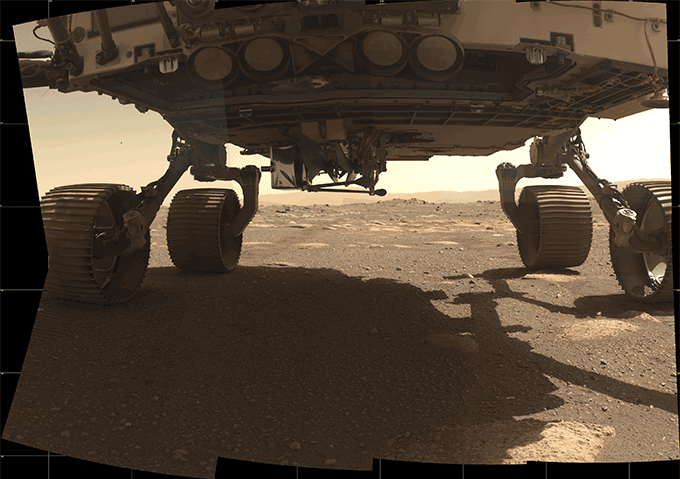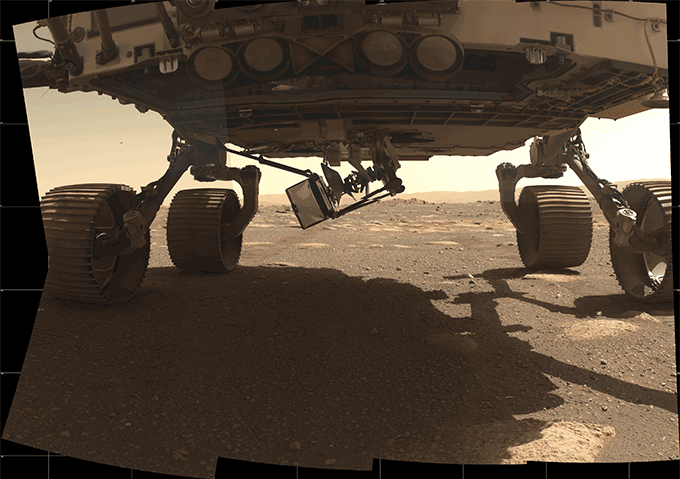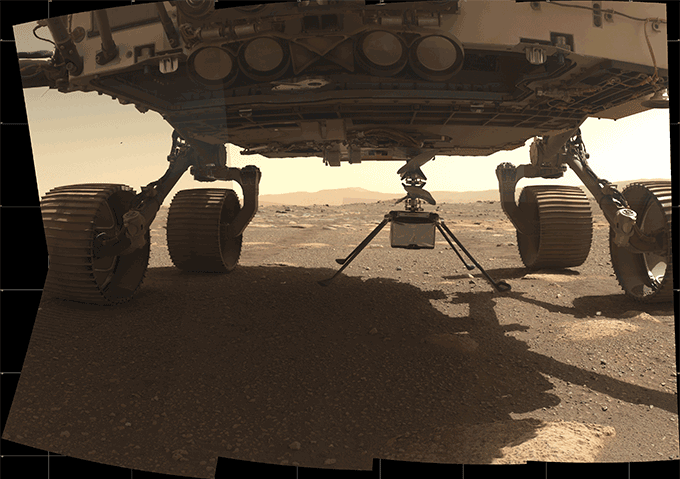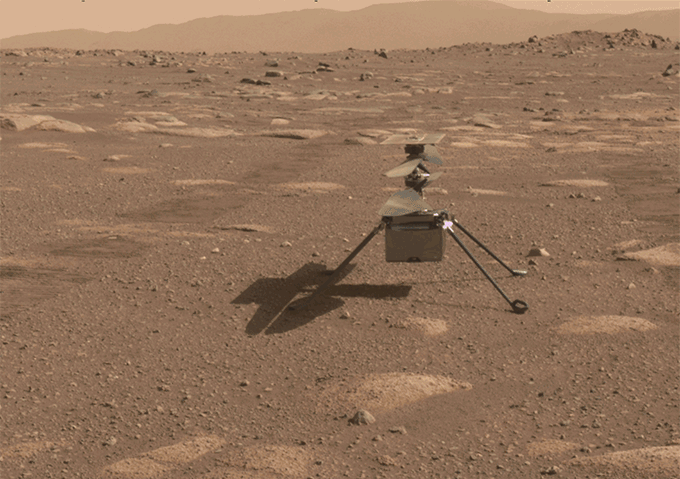
NASA has simply flown a helicopter on Mars. Named Ingenuity, the craft hovered for about 40 seconds above the Red Planet’s floor. This marks the primary flight of a spacecraft on a planet apart from Earth.
In the wee hours on April 19, the helicopter spun its rotor blades and ascended into the skinny Martian air. It rose about three meters (or 10 ft) above the bottom. After pivoting to take a look at NASA’s Perseverance rover and snap an image of its personal shadow, the small copter settled again right down to the bottom.
“Goosebumps. It looks just the way we had tested it,” mentioned MiMi Aung in an information briefing after the flight. Aung is Ingenuity’s challenge supervisor. When this engineer noticed the copter’s check trial on Mars, she described it as an “absolutely beautiful flight. I don’t think I can ever stop watching it over and over again.”
At about 6:35 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) on April 19, a hush fell over Ingenuity’s mission management room. Data from the flight have been simply beginning to arrive right here at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Pasadena, Calif. Håvard Grip is Ingenuity’s chief pilot. In quick order, he introduced: “Confirmed that Ingenuity has performed its first flight — the first flight of a powered aircraft on another planet.”
At as soon as, cheers erupted all through the room.
“It’s amazing, brilliant. Everyone is super excited,” mentioned Taryn Bailey. “I would say it’s a success.” Bailey is a mechanical engineer and staff member.
The flight had been delayed for slightly more than per week when a check of the rotor blades confirmed issues. The engineers up to date the plane’s software program. The flight was again on.
Following Ingenuity’s temporary time aloft, Aung congratulated her staff. “Take that moment [to celebrate],” she informed them. Then, she added, “Let’s get back to work and more flights.”
Testing now, science later
This first-ever flight was a check of the technology. It’s including “a tool we haven’t been able to use,” mentioned Thomas Zurbuchen. He’s NASA’s affiliate administrator for its science missions division. Now that NASA is aware of the helicopter works, he added, this software shall be “available for all of our missions at Mars.”
Ingenuity’s mission is about to final 30 Martian days. (That equals some 31 Earth days.) During that point, it gained, in reality, do any science. But its success proves that powered flight is feasible in Mars’ skinny ambiance. Future aerial automobiles on the Red Planet might assist rovers or human astronauts scout secure paths by means of unfamiliar landscapes. Or a copter would possibly survey tough terrain {that a} rover can’t traverse.
When NASA first started testing early prototypes of a Mars helicopter at JPL in 2014, it wasn’t clear that flying on Mars would even be potential, Aung mentioned. “It’s challenging for many different reasons.”
Though Mars’ gravity is about one-third that on Earth, the density of the air on Mars is simply a few hundredth that at sea degree on our planet. It’s troublesome for a helicopter’s blades to push towards such skinny air onerous and nonetheless get off the bottom.
Amelia Quon is an Ingenuity engineer at JPL. At an information briefing on April 9, she recalled that some individuals had “doubted we could generate enough lift to fly in that thin Martian atmosphere.” So for 5 years, she and her staff put prototypes — and in the end Ingenuity itself — by means of a battery of checks.
Explains Quon, “My job … was to make Mars on Earth, and enough of it that we could actually fly our helicopter in it.” Her staff’s Mars simulation chamber could possibly be emptied of Earth’s air and pumped filled with carbon dioxide at Mars-like densities. Some variations of the helicopter have been suspended from the ceiling to simulate Mars’ decrease gravity. Wind speeds as much as 30 meters per second (67 miles per hour) have been simulated with a financial institution of about 900 laptop followers blowing on the helicopter.
The remaining design known as a lightweight craft; it weighs a mere 1.8 kilograms (4 kilos) on Earth. (Its mass shall be similar on Mars, though its weight isn’t.) Its wingspan runs roughly 1.2 meters (3.9 ft). Those rotors are longer than what an analogous car would wish to fly on Earth. They rotate quicker, too — some 2,400 occasions a minute. By the time Ingenuity hitched a journey to Mars on the Perseverance rover in July 2020, the engineers have been assured the helicopter might fly on Mars.
The rover’s function
Perseverance landed at a website known as Jezero crater on February 18. Folded up and lined by a protecting protect beneath the rover’s stomach was Ingenuity.
Over the subsequent few weeks, Perseverance motored in the hunt for a flat spot for the whirlybird to launch. It discovered one, and Ingenuity slowly unfolded itself and was lowered gently to the bottom on April 3. The rover then drove away rapidly to get Ingenuity out of its shadow. A photovoltaic panel might now cost the helicopter’s batteries sufficient to make it by means of the freezing Martian nights.
On April 8 and 9, Ingenuity unfolded its rotor blades and examined their skill to spin. After trouble-shooting the software program downside and retesting the rotor blades on April 16, NASA gave an inexperienced gentle to fly at roughly 3:30 a.m. EDT on April 19. That’s about 12:30 p.m. Mars time. Such an early afternoon liftoff would give the craft’s photovoltaic panel sufficient time to cost up to its batteries for the flight. Perseverance’s climate sensors are additionally prompt that the winds could be solely about six meters per second (13 miles per hour).
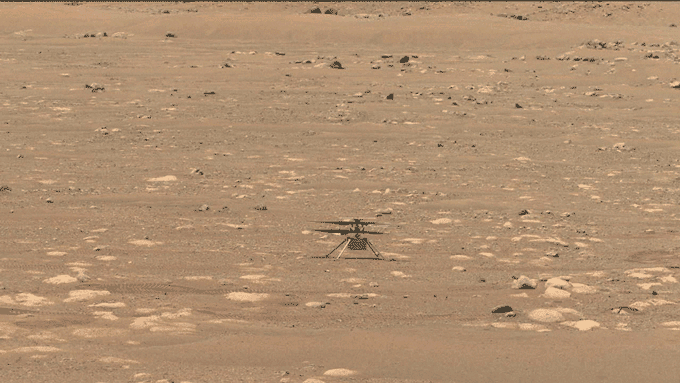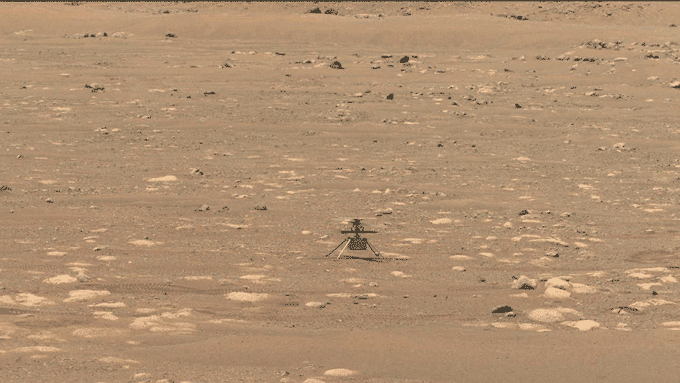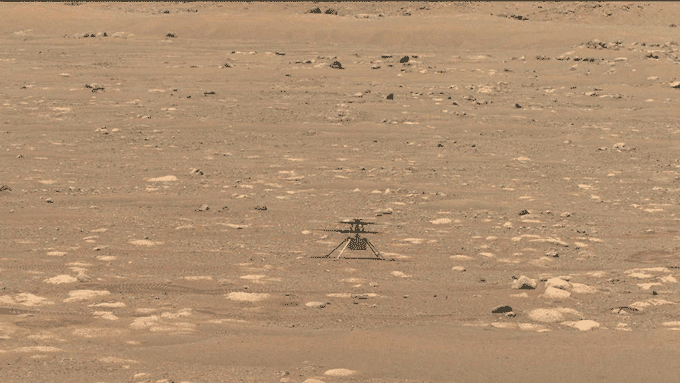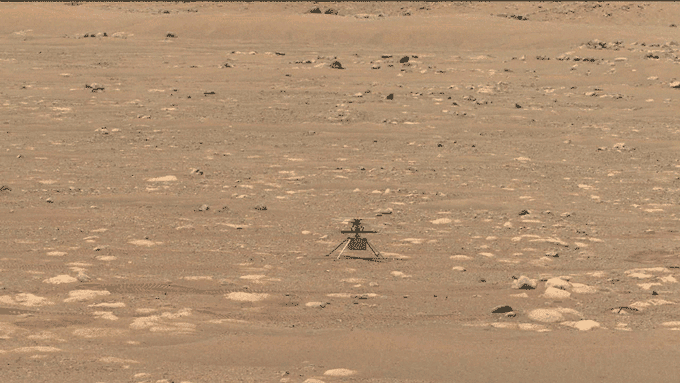
Ingenuity needed to pilot itself. Mars is much sufficient from Earth that gentle alerts take about a quarter-hour to journey between the 2 planets. For that purpose, NASA engineers couldn’t handle second-to-second steering challenges. And Mars’ skinny air makes the helicopter troublesome to steer. “Things happen too quickly for a human pilot to react to it,” Quon notes.
Perseverance filmed the flight from about 65 meters (virtually 215 ft) away. Ingenuity additionally filmed its flight using two units of cameras. Downward dealing with navigation cameras captured the view under it in black and white as color cameras scanned the horizon.
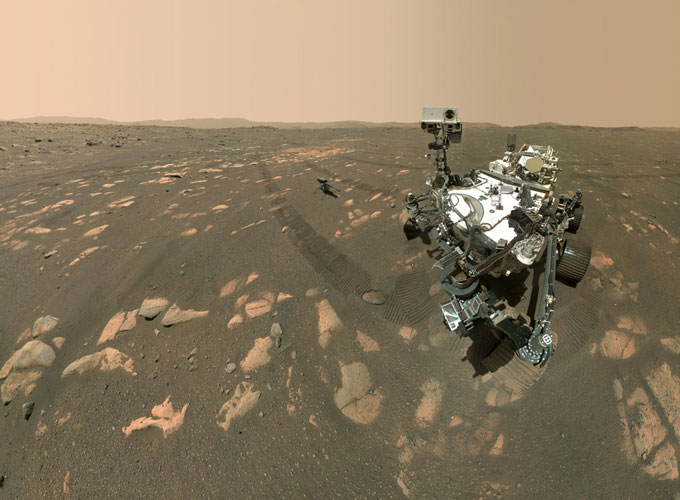

Now that this primary flight went nicely, NASA engineers hope to arrange as many as 4 more flights, presumably beginning as quickly as April 22. Each shall be slightly bitted more daring — and dangerous, Aung says. “We are going to continually push all the way to the limit of this rotorcraft.” And every flight shall be a nail-biter. Just one dangerous touchdown might finish issues as Ingenuity has no approach to proper itself after a fall.
In truth, which may be the best way the mission ends. “Ultimately, we expect the helicopter will meet its limit,” Aung admitted at an April 19 information briefing. Even if it wipes out in a crash, her engineering staff could have discovered worthwhile classes.
Eventually, Perseverance will drive off, forsaking the little helicopter that might. The rover will soldier on to proceed with its personal mission: to seek indicators of a previous life in Jezero crater and to retailer rocks for a future journey to Earth.
Check below for more related contents:






